6 Slim Disks
The Shakura–Sunyaev and Novikov–Thorne models of thin disks assume that accretion is radiatively efficient. This assumption means that all the heat generated by viscosity at a given radius is immediately radiated away. In other words, the viscous heating is balanced by the radiative cooling locally and no other cooling mechanism is needed. This assumption can be satisfied as long as the accretion rate is small. At some luminosity (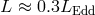 ), however, the radial velocity is large, and the disk is thick
enough, to trigger another mechanism of cooling: advection. It results from the fact that the
viscosity-generated heat does not have sufficient time to transform into photons and leave the
disk before being carried inwards by the motion of the gas. The higher the luminosity, the
more significant advective cooling is. At the highest luminosities, it becomes comparable to
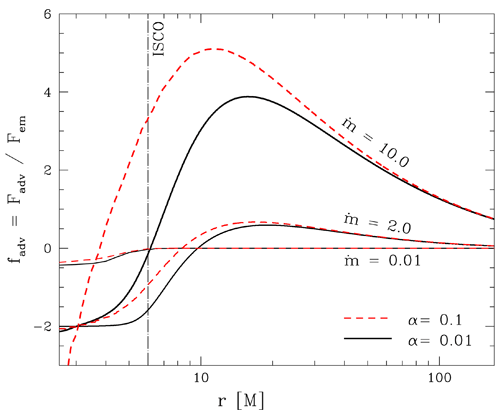
the radiative cooling (see Figure 8
), however, the radial velocity is large, and the disk is thick
enough, to trigger another mechanism of cooling: advection. It results from the fact that the
viscosity-generated heat does not have sufficient time to transform into photons and leave the
disk before being carried inwards by the motion of the gas. The higher the luminosity, the
more significant advective cooling is. At the highest luminosities, it becomes comparable to
the radiative cooling (see Figure 8 ), and the standard, thin disk approach can no longer be
applied.
), and the standard, thin disk approach can no longer be
applied.
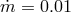 ,
,
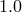 and
and 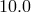 (here,
(here, 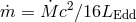 ). Profiles for
). Profiles for  and
and 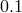 are presented with
solid black and dashed red lines, respectively. The fraction
are presented with
solid black and dashed red lines, respectively. The fraction 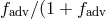 ) of heat generated by
viscosity is carried along with the flow. In regions with
) of heat generated by
viscosity is carried along with the flow. In regions with 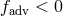 the advected heat is released.
Image reproduced by permission from [269
the advected heat is released.
Image reproduced by permission from [269 ].
]. The problem of accretion with an additional cooling mechanism has to be treated in a different way than
radiatively efficient flows. Without the assumptions of radiative efficiency and Keplerian angular
momentum, it is no longer possible to find an analytic solution to the system of equations presented in
Section 5.1. Instead, one has to solve a two-dimensional system of ordinary differential equations (95 ) with
a critical point – the radius at which the gas velocity exceeds the local speed of sound (the sonic radius).
This was first done in the pseudo-Newtonian limit by Abramowicz [8], who forged the term “slim
disks”. It has since been done using a fully relativistic treatment by Beloborodov [40]. Recently,
Sadowski [268] constructed slim disk solutions for a wide range of parameters applicable to X-ray
binaries.
) with
a critical point – the radius at which the gas velocity exceeds the local speed of sound (the sonic radius).
This was first done in the pseudo-Newtonian limit by Abramowicz [8], who forged the term “slim
disks”. It has since been done using a fully relativistic treatment by Beloborodov [40]. Recently,
Sadowski [268] constructed slim disk solutions for a wide range of parameters applicable to X-ray
binaries.
These slim disks are in some sense more physical than thin disks and offer a more general set of
solutions, while in the limit of low accretion rates they converge to the standard thin disk solutions. Slim
disks are more physical in that they extend down to the black hole horizon, as opposed to thin disks that
formally terminate at the ISCO. Slim disks are more general in that they may rotate with an angular
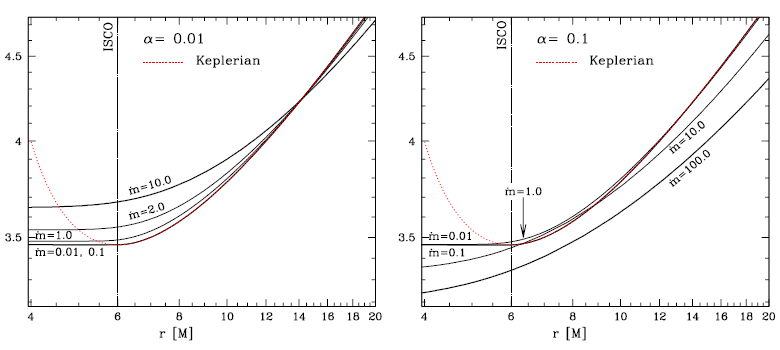
momentum profile significantly different than the Keplerian one – the higher the accretion rate, the more
significant the departure (see Figure 9 ). The disk thickness also increases with the accretion rate. For rates
close the Eddington limit, the maximal
). The disk thickness also increases with the accretion rate. For rates
close the Eddington limit, the maximal 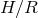 ratio reaches 0.3. Finally, the flux emerging from the
slim disk surface is modified by the advection. At high luminosities, a large fraction of the
viscosity-generated heat is advected inward and released closer to the black hole or not released at all.
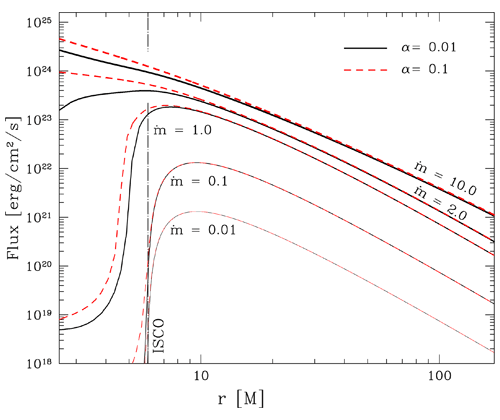
As a result, the slope of the radial flux profile changes, and radiation is even emitted from
within the ISCO (see Figure 10
ratio reaches 0.3. Finally, the flux emerging from the
slim disk surface is modified by the advection. At high luminosities, a large fraction of the
viscosity-generated heat is advected inward and released closer to the black hole or not released at all.
As a result, the slope of the radial flux profile changes, and radiation is even emitted from
within the ISCO (see Figure 10 ). Due to the increasing rate of advection, the efficiency of
transforming gravitational energy into radiative flux decreases with increasing accretion rate.
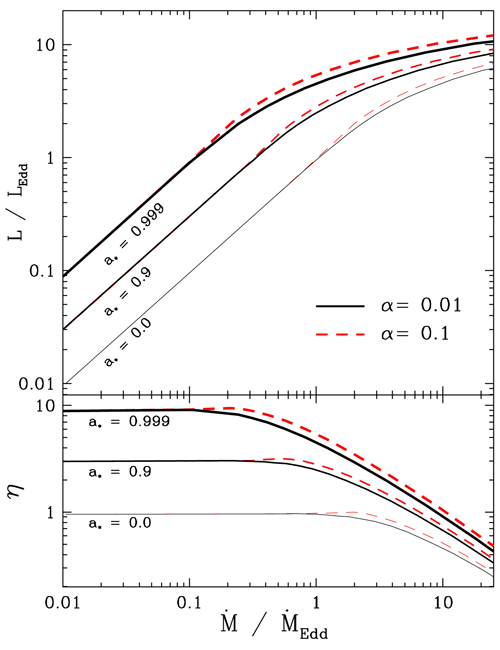
Despite highly super-Eddington accretion rates, the disk luminosity remains only moderately
super-Eddington (see Figure 11
). Due to the increasing rate of advection, the efficiency of
transforming gravitational energy into radiative flux decreases with increasing accretion rate.
Despite highly super-Eddington accretion rates, the disk luminosity remains only moderately
super-Eddington (see Figure 11 ). The Eddington luminosity may be exceeded because the
geometry of the flow is not spherical and the classical definition of this quantity does not apply –
most of the accretion takes place in the equatorial plane while the radiation escapes vertically.
Thus, the radiation is not capable of stopping the inflow, though it may cause outflows from the
surface.
). The Eddington luminosity may be exceeded because the
geometry of the flow is not spherical and the classical definition of this quantity does not apply –
most of the accretion takes place in the equatorial plane while the radiation escapes vertically.
Thus, the radiation is not capable of stopping the inflow, though it may cause outflows from the
surface.
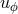 ) for
) for 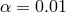 (left) and
(left) and 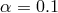 (right
panel) for different accretion rates (as a reminder,
(right
panel) for different accretion rates (as a reminder, 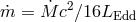 ), showing the departures from
the Keplerian profile. These plots are for a non-rotating black hole. Image reproduced by permission
from [270
), showing the departures from
the Keplerian profile. These plots are for a non-rotating black hole. Image reproduced by permission
from [270 ], copyright by ESO.
], copyright by ESO. : 0.01 (black solid), 0.1 (red dashed lines). For each value of
: 0.01 (black solid), 0.1 (red dashed lines). For each value of 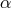 there are five
lines corresponding to the following mass accretion rates:
there are five
lines corresponding to the following mass accretion rates: 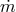 = 0.01, 0.1, 1.0, 2.0 and 10.0 (as a
reminder,
= 0.01, 0.1, 1.0, 2.0 and 10.0 (as a
reminder, 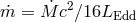 ). The black hole mass is
). The black hole mass is 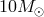 . Image reproduced by permission
from [270], copyright by ESO.
. Image reproduced by permission
from [270], copyright by ESO.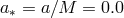 ,
,  ,
, 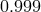 ) and two values of
) and two values of 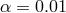 (black) and 0.1 (red line).
Bottom panel: efficiency of accretion
(black) and 0.1 (red line).
Bottom panel: efficiency of accretion 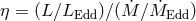 (here
(here 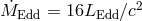 ). Image
reproduced by permission from [269].
). Image
reproduced by permission from [269].